Website: http://homeiu.com/
Email: homeiu@tusco.net
Phone: (330) 243-2718
Inspector:
Marcus Sellards
| Sample Report |
| Client(s): |
Your inspection |
| Property address: |
1234 your home |
| Inspection date: |
Jan 24 2006 | This report published on 4/4/2006 12:55:15 PM EDT
This report is the exclusive property of this inspection
company and the client(s) listed in the report title. Use of this report by any
unauthorized persons is prohibited.
How to Read this Report
This
report is organized by the property's functional areas. Within each functional
area, descriptive information is listed first and shown in bold type. Items of
concern follow descriptive information and are shown as follows:
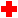 |
Safety |
Poses a risk of injury or death |
 |
Major defect |
Correction could involve a major repair expense
or replacement |
 |
Repair/Replace |
Recommend repairing or replacing |
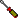 |
Repair/Maintain |
Recommend repair and/or maintenance |
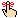 |
Minor defect |
Correction likely involves only a minor
expense |
 |
Maintain |
Recommend ongoing maintenance |
 |
Evaluate |
Recommend evaluation by a qualified
specialist |
 |
Monitor |
Recommend monitoring in the future |
 |
Comment |
For your
information | Concern items are sorted by the types
listed above. Click here for a
glossary of building construction terms. Contact
your inspector if there are terms that you do not understand, or visit the
glossary of construction terms at http://www.reporthost.com/glossary.asp
Table of Contents
Exterior
Roof
SHED/GARAGE
Electric
service
Water heater
Plumbing and
laundry
Crawl space
Kitchen
Bathrooms
Bedroom
Living/Family
room
Footing material:
None
Foundation material:
Poured in place concrete, Concrete block
Foundation material: Oured cement and cement
block
Apparent wall structure: Wood frame
Wall covering: Wood panels
Driveway material: Gravel, Dirt
Sidewalk material: None
Exterior door material: Wood panel
   |
1) Guardrails are missing from one or more
sections of the front porch or elevated surfaces with high drop-offs. This
is a safety hazard due to the risk of falling. Standard building practices
require guardrails to be installed at drop-offs higher than 30 inches, but
in some cases it is advised to install them at shorter drop-offs. A
qualified contractor should evaluate and install guardrails as necessary
and as per standard building practices.
Location: front porch.
|
   |
2) One or more light fixtures located in
"wet" or "damp" locations have no visible rating for use in wet locations.
This is a safety hazard due to the risk of shock. A qualified electrician
should evaluate and replace light fixtures as necessary and as per
standard building practices.
Located in the well house. |
   |
3) Wire splices are exposed due to not
being contained in a covered junction box. This is a safety hazard due to
the risk of shock and fire. A qualified electrician should evaluate and
make repairs as necessary. For example, install securely mounted junction
boxes with cover plates where needed to contain wiring splices.
Location: Outside well house fuse box and tank.
|
   |
4) The deck is unstable in one or more
areas due to lack of diagonal bracing. This is a safety hazard since
severe movement may cause the railing to collapse. A qualified contractor
should evaluate and make repairs as necessary.
|
  |
5) Water supply pipes are routed outside
and are subject to freezing. The client(s) should ask the property
owner(s) if inside shut-off valves exist for these supply pipes. If unable
to determine if shut-off valve(s) exist, or if none do, then a qualified
plumber should evaluate and install interior shut-off valves as necessary
to prevent pipes from freezing and bursting.
Location: southeast
corner of home.
|
 |
6) One or more large trees are very close
the foundation. Tree roots can cause significant structural damage to
foundations. Recommend having a qualified tree service contractor or
arborist remove trees as necessary to prevent damage to the structure's
foundation.
|
 |
7) The perimeter grading slopes towards the
structure in one or more areas. This can result in water accumulating
around the structure's foundation, or in basements and crawl spaces if
they exist. Accumulated water is a conducive condition to wood destroying
insects and organisms. Wet soil may also cause the foundation to settle
and possibly fail over time. Recommend grading soil so it slopes down and
away from the structure with a slope of at least 5% (10% or better is
optimal) for at least 6 feet.
|
 |
8) One or more downspouts are missing. This
can result in water accumulating around the structure's foundation, or in
basements and crawl spaces if they exist. Accumulated water is a conducive
condition to wood destroying insects and organisms, and may also cause the
foundation to settle and possibly fail over time. A qualified contractor
should install downspout(s) where missing. Also recommend installing
extensions such as splashblocks or tie-ins to underground drain lines as
necessary to carry rainwater away from the house. |
 |
9) One or more gutters are missing. This
can result in water accumulating around the structure's foundation, or in
basements and crawl spaces if they exist. Accumulated water is a conducive
condition to wood destroying insects and organisms, and may also cause the
foundation to settle and possibly fail over time. A qualified contractor
should install gutters and downspouts where missing. Also, extensions such
as splashblocks or tie-ins to underground drain lines should be installed
as necessary to carry rain water away from the house.
|
 |
10) One or more crawl space vent screens
are missing. Animals such as vermin or pets may enter the crawl space and
nest, die and/or leave feces and urine. A qualified contractor should
install screens where missing using screen material such as "hardware
cloth" with 1/4 inch minimum gaps.
Location: East side of house.
|
 |
11) One or more wooden deck support posts
are in contact with soil. This is a conducive condition for wood
destroying insects and organisms. However no damage from wood destroying
insects or organisms was found. Standard building practices require that
there be at least 6" of space between any wood and the soil below, even if
the wood is treated. If possible, soil should be removed or graded so a 6"
clearance is maintained. Otherwise recommend installing borate based Impel rods to prevent rot.
|
  |
12) One or more moderate cracks (1/8 inch
to 3/4 inch) were found in the foundation. These may be a structural
concern, or an indication that settlement is ongoing. The client(s) should
consider hiring qualified contractors and/or engineers as necessary for
further evaluation. Such contractors may include:
These were
located at the supporting cement blocks which are also starting to lean
outward.
Foundation repair contractors who may prescribe repairs, and will give
cost estimates for prescribed repairs
Masonry contractors who repair and/or replace brick veneer
Geotechnical engineers who attempt to determine if settlement is
ongoing, and what the cause of the settlement is
Structural engineers who determine if repairs are necessary, and
prescribe those repairs
At a minimum, recommend sealing cracks to
prevent water infiltration. Numerous products exist to seal such cracks
including:
Hydraulic cement. Requires chiseling a channel in the crack to apply.
See http://www.quickrete.com/catalog/HydraulicWater-StopCement.html
for an example.
Resilient caulks (easy to apply). See http://www.quickrete.com/catalog/GrayConcreteRepair.html
for an example.
Epoxy sealants (both a waterproof and structural repair). See http://www.mountaingrout.com/ for examples of these
products.
|
 |
13) Vegetation such as trees, shrubs and/or
vines are in contact with or less than one foot from the structure's
exterior. Vegetation can serve as a conduit for wood destroying insects
and may retain moisture against the exterior after it rains. Vegetation
should be pruned and/or removed as necessary to maintain a one foot
clearance between it and the structure's exterior.
Location: West
side of deck. |
 |
14) Window glazing putty at one or more
windows is missing and/or deteriorated. Putty should be replaced and/or
installed where necessary. For more information on replacing window putty,
visit: http://www.oldhouseweb.com/stories/Detailed/12216.shtml
|
 |
15) Recommend cleaning deck(s) and
railing(s) and treating with a preservative claiming to waterproof, block
ultraviolet light, and stop mildew. Consumer Reports recommends
these products:
Cabot Decking Stain and PTW Stain
Olympic Water Repellent Deck Stain
Thompson's House and Deck Stain
Wolman PTW Deck Stain
Akzo Sikkens Cetol DEK
Benjamin Moore Moorwood Clear Wood Finish
DAP Woodlife Premium
Olympic Natural Look Protector Plus |
 |
16) Caulk is missing or deteriorated in
some areas and should be replaced and/or applied where necessary. For more
information on caulking, visit The Ins and Outs of Caulking. |
 |
17) One or more outside faucets were not
evaluated due to their being winterized with covers, and are excluded from
this inspection. |
Roof inspection
method: Traversed
Roof type:
Gable, A-frame
Roof covering:
Asphalt or fiberglass composition shingles
Estimated age of roof: 8-12 years
Gutter & downspout material: None
Roof ventilation: Unable to determine (no access to attic spaces)
 |
18) One or more "rubber boot" flashings are
lifting at the base or are improperly installed so that water or vermin
intrusion may occur. A qualified contractor should make repairs as
necessary, such as permanently fastening down the lifted edge(s), or
reinstalling flashings. |
 |
19) Debris such as leaves, needles, seeds,
etc. have accumulated on the roof. This is a conducive condition for wood
destroying insects and organisms since water may not flow easily off the
roof, and may enter gaps in the roof surface. Leaks may occur as a result.
Debris should be cleaned from the roof now and as necessary in the future.
|
 |
20) Moss is growing on the roof. As a
result, shingles may lift or be damaged. Leaks may result and/or the roof
surface may fail prematurely. This is a conducive condition for wood
destroying insects and organisms. Efforts should be taken to kill the moss
during its growing season (wet months). Typically zinc-based chemicals are
used for this, and must be applied periodically. For information on
various moss treatment products and their pros and cons, visit http://bryophytes.science.oregonstate.edu/page24.htm.
|
 |
21) Trees are overhanging roof and are
within 10 feet of roof vertically. This is a conducive condition for wood
destroying insects and organisms since organic debris such as leaves or
needles are more likely to accumulate on the roof surface. Accumulated
debris may cause water to enter gaps in the roof surface and leak into
attic and/or interior spaces. Trees should be pruned so they are at least
10 feet above roof, or don't overhang the roof. |
 |
22) The roof was partially obscured by
accumulated debris and couldn't be fully evaluated.
|
 |
23) Supports posts are in direct contact
with the ground and are subect to rot and pest infiltraation.
|
 |
24) Much of the garage, include areas
around the interior perimeter and in the center are excluded from this
inspection due to lack of access from stored items.
|
Primary service
type: Overhead
Primary service
overload protection type: Circuit breakers,
Fuses
Service amperage (amps): 100
Service voltage (volts): 120/240
Location of main service switch:
West wall of bedroom
Location of
sub panels: West wall of bedroom
Location of main disconnect: No single main
disconnect, use all breakers in main service panel
System ground: Ground rod(s) in
soil
Service entrance conductor material: Copper
Main disconnect rating (amps):
100
System ground: Ground rod(s) in soillocated unser deck at west side of
house
Branch circuit wiring type: Copper
Solid strand aluminum branch circuit
wiring present: Can't verify
Branch circuit wiring type: Copper
Smoke detectors present: No
Solid strand aluminum branch circuit wiring
present: Can't verify
  |
25) The service panel in the outside well
house is unsafe and rusted. This a potential fire hazard. A qualified
electrician should evaluate and repair if necessary.
|
   |
26) The service drop wires are less than 12
feet above the driveway. This is a safety hazard due to the risk of shock.
A qualified electrician and/or the utility company should evaluate and
repair as necessary.
|
   |
27) Inadequate working space exists for the
sub-panel. Standard building practices require the following
clearances:
An area 30 inches wide by 3 feet deep exists in front of the panel
The panel is at least 5 1/2 feet above the floor
There is at least 6 feet 6 inches of headroom in front of the
panel
The wall below the panel is clear to the floor
A qualified
contractor and/or electrician should evaluate and make modifications as
necessary. |
   |
28) The electric service to this property
appears to be rated at substantially less than 200 amps, and may be
inadequate for the client(s) needs. Recommend consulting with a qualified
electrician about upgrading to a 200 amp service. |
  |
29) The sub-panel couldn't not be evaluated
properly due to lack of access from walls encasing the panel to closely..
This panel wasn't fully evaluated. Repairs should be made so the panel
cover can be easily removed. |
Estimated age:
10+ years
Type: Tank
Energy source: Electricity
Capacity (in gallons):
30
Manufacturer: U.S. Craftmaster
Model: E1E33LD0454
  |
30) Corrosion was found in one or more
areas on the water heater. The water heater may be failing. A qualified
plumbing contractor should evaluate and replace or repair water heater if
necessary. |
  |
31) The estimated useful life for most
water heaters is 8 to 12 years. The inspector was unable to determine the
age of the water heater due to the manufacturer's label being obscured, no
serial number being visible, or the serial number not clearly indicating
the age. The clients should be aware that this water heater may be near,
at, or beyond its useful life and may need replacing at any time.
Recommend attempting to determine the water heater's age, and budgeting
for a replacement if necessary. |
 |
32) The water heater was turned off at the
time of the inspection. For example, circuit breaker turned off, gas
supply turned off or pilot light turned off. The inspector was unable to
fully evaluate the water heater. |
Location of main
water shut-off valve: Under south side of house and in
well house
Water service: Private
Service pipe material: Galvanized steel, Lead
Vent pipe material:
Not visible
Drain pipe material:
Plastic
Waste pipe material:
Plastic
  |
33) Copper water supply pipes in homes
built prior to 1986 may be joined with solder that contains lead. Lead is
a known health hazard, especially for children. Laws were passed in 1985
prohibiting the use of lead in solder, but prior to that solder normally
contained about 50 percent lead. The client(s) should be aware of this,
especially if children will be living in this structure. Evaluating for
the presence of lead in this structure is not included in this inspection.
The client(s) should consider having a qualified lab test for lead, and if
necessary take steps to reduce or remove lead from the water supply.
Various solutions such as these may be advised:
Flush water taps or faucets. Do not drink water that has been sitting
in the plumbing lines for more than six hours.
Install appropriate filters at points of use.
Use only cold water for cooking and drinking. Hot water dissolves lead
more quickly than cold water.
Use bottled or distilled water.
Treat well water to make it less corrosive.
Have a qualified plumbing contractor replace supply pipes and/or
plumbing components as necessary.
For more information visit: http://www.cpsc.gov/CPSCPUB/PUBS/5056.html and http://www.epa.gov/safewater/lead/index.html |
 |
34) Neither the clothes washer nor dryer
were operated or evaluated. They are excluded from this inspection. |
| |
35) Water was turned off or winterized not
allowing for a proper inspection of said items. |
Inspection method:
Partially traversed
Insulation
material underneath floor above: None
visible
Pier or support post material: Concrete, Masonry
Beam material: Solid wood
Floor structure above: Solid wood joists
Vapor barrier present:
Not visible
  |
36) Standing water was found in one or more
sections of the crawl space. Accumulated water is a conducive condition
for wood destroying insects and organisms and should not be present in the
crawl space. A qualified contractor who specializes in drainage issues
should evaluate and repair as necessary. Typical repairs for preventing
water from accumulating in crawl spaces include:
Repairing, installing or improving rain run-off systems (gutters,
downspouts and extensions or drain lines)
Improving perimeter grading
Repairing, installing or improving underground footing and/or curtain
drains
Ideally, water should not enter crawl spaces, but if water
must be controlled after it enters the crawl space, then typical repairs
include installing trenches, drains and/or sump pump(s) in the crawl
space. |
 |
37) No vapor barrier is installed in some
areas. This is a conducive condition for wood destroying insects and
organisms due to the likelihood of water evaporating into the structure
from the soil. A qualified contractor should install a vapor barrier where
missing. Standard building practices require the following:
The soil below the vapor barrier should be smooth and free from sharp
objects.
Seams should overlap a minimum of 12 inches.
The vapor barrier should lap up onto the foundation side
walls.
Better building practices require that:
Seams and protrusions should be sealed with a pressure sensitive
tape.
The vapor barrier should be caulked and attached tightly to the
foundation side walls. For example, with furring strips and masonry nails.
|
 |
38) No insulation under floor in crawl
space in some areas. Recommend that a qualified contractor install R19 or
better (6" thick fiberglass batt) insulation below floor where missing for
energy efficiency. |
 |
39) Water supply pipes are uninsulated.
Recommend insulating pipes as necessary for better energy efficiency and
to prevent water pipes from freezing. |
 |
40) Large tree roots are growing underneath
the southeast crawl space entrance. This could lead to problems with
support members shifting and waste pipe clogging.
|
 |
41) Cellulose-based debris such as wood
scraps, form wood, cardboard and/or paper were found in crawl space. All
cellulose-based debris should be removed to avoid attracting wood
destroying insects. |
 |
42) Some crawl space areas were
inaccessible due to low height (less than 18 inches), ductwork or pipes
blocking, standing water, and/or stored items. These areas are excluded
from this inspection. |
: Water was turned off not allowing for proper inspection of
kitchen.
   |
43) One or more electric receptacles that
serve countertop surfaces within six feet of a sink appear to have no
ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protection. This is a safety
hazard due to the risk of shock. A qualified electrician should evaluate
to determine if GFCI protection exists, and if not, repairs should be made
so that all receptacles that serve countertop surfaces within six feet of
sinks have GFCI protection. For example, install GFCI receptacles or
circuit breaker(s) as needed. |
 |
44) The refrigerator, stove and oven all
operated properly. |
: Water was turned off not allowing a complete inspection of the
bathroom.
   |
45) One or more electric receptacles that
serve countertop surfaces within six feet of a sink appear to have no
ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protection. This is a safety
hazard due to the risk of shock. A qualified electrician should evaluate
to determine if GFCI protection exists, and if not, repairs should be made
so that all receptacles that serve countertop surfaces within six feet of
sinks have GFCI protection. For example, install GFCI receptacles or
circuit breaker(s) as needed. |
 |
46) One or more bathrooms with a shower do
not have an exhaust fan installed. Moisture accumulation will occur and
may damage the structure. Even if the bathroom has a window that opens, it
likely does not provide adequate ventilation, especially during cold
weather when the window is closed. A qualified contractor should install
exhaust fans as per standard building practices where missing in bathrooms
with showers. |
  |
47) No smoke alarms are visible. This is a
safety hazard. A qualified electrician should install smoke alarms as per
standard building practices (functioning one exists in hallways leading to
bedrooms, and in each bedroom, etc.). For more information, visit http://www.cpsc.gov/cpscpub/pubs/5077.html |
 |
48) One or more rooms that are considered
living spaces appear to have no visible source of heat. The client(s)
should consult with the property owner(s) regarding this, and if
necessary, a qualified contractor should evaluate and install heat
source(s) as necessary. |
 |
49) Due to furniture being present, some
areas of the bedroom were not visible. |
   |
50) Extension cords are being used as
permanent wiring in one or more areas. They should only be used for
portable equipment on a temporary basis. Using extension cords as
permanent wiring poses a fire and shock hazard, and is an indication that
wiring is inadequate and should be updated. Extension cords may be
undersized. Connections may not be secure, resulting in power
fluctuations, damage to equipment, and sparks that could start a fire.
Extension cords should be removed as necessary, or a qualified electrician
should evaluate and make repairs as necessary. For example, install
additional circuits and/or electric receptacles. |
  |
51) No smoke alarms are visible. This is a
safety hazard. A qualified electrician should install smoke alarms as per
standard building practices (functioning one exists in hallways leading to
bedrooms, and in each bedroom, etc.). For more information, visit http://www.cpsc.gov/cpscpub/pubs/5077.html |
  |
52) Screen(s) in one or more windows are
missing. The client(s) should ask the property owner(s) about this.
Screens are often removed for window cleaning and they may be stored
somewhere. If not, then recommend installing screens where missing. |
 |
53) Screen(s) in one or more windows are
torn or have holes in them. Screens should be replaced where necessary.
|
 |
54) One or more rooms that are considered
living spaces appear to have no visible source of heat. The client(s)
should consult with the property owner(s) regarding this, and if
necessary, a qualified contractor should evaluate and install heat
source(s) as necessary. |
|